Page 20 - PLATINO EDUCA
P. 20
20 is responsible for executive functions: the ability to plan, organize and regulate our
behavior based on the goal that we want to achieve. This function allows us to inhibit
and control harmful tendencies or impulses, modify behaviors and control attention. It is
also responsible for working memory and provides us with mental flexibility to consider
new alternatives when solving problems. Thanks to the executive function we can link
present motivations to future objectives, in other words, we can establish long-term
goals. In turn, it is what allows us to sacrifice (or say no to) immediate rewards in favor
of other more valuable goals.
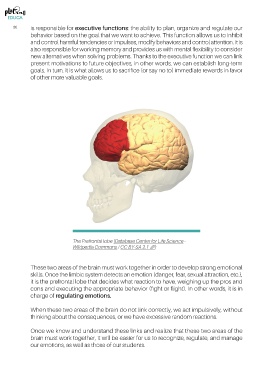
The Prefrontal lobe (Database Center for Life Science -
Wikipedia Commons / CC BY-SA 2.1 JP)
These two areas of the brain must work together in order to develop strong emotional
skills. Once the limbic system detects an emotion (danger, fear, sexual attraction, etc.),
it is the prefrontal lobe that decides what reaction to have, weighing up the pros and
cons and executing the appropriate behavior (fight or flight). In other words, it is in
charge of regulating emotions.
When these two areas of the brain do not link correctly, we act impulsively, without
thinking about the consequences, or we have excessive random reactions.
Once we know and understand these links and realize that these two areas of the
brain must work together, it will be easier for us to recognize, regulate, and manage
our emotions, as well as those of our students.