Page 19 - PLATINO EDUCA
P. 19
our emotions, reactions and, therefore, our behaviors do not derive solely from the 19
environment or particular circumstances, but from our brains.
In order to detect, regulate and facilitate our emotions, we must consider two fundamental
areas of our brain:
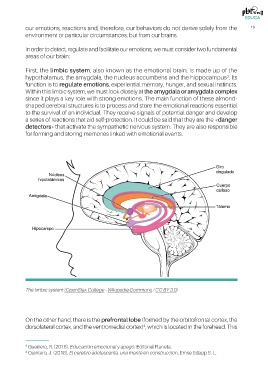
First, the limbic system, also known as the emotional brain, is made up of the
hypothalamus, the amygdala, the nucleus accumbens and the hippocampus . Its
3
function is to regulate emotions, experiential memory, hunger, and sexual instincts.
Within this limbic system, we must look closely at the amygdala or amygdala complex
since it plays a key role with strong emotions. The main function of these almond-
shaped cerebral structures is to process and store the emotional reactions essential
to the survival of an individual. They receive signals of potential danger and develop
a series of reactions that aid self-protection. It could be said that they are the «danger
detectors»that activate the sympathetic nervous system. They are also responsible
for forming and storing memories linked with emotional events.
The limbic system (OpenStax College - Wikipedia Commons / CC BY 3.0)
On the other hand, there is the prefrontal lobe (formed by the orbitofrontal cortex, the
4
dorsolateral cortex, and the ventromedial cortex) , which is located in the forehead. This
3 Guerrero, R. (2018). Educación emocional y apego. Editorial Planeta.
4 Quintero, J. (2018). El cerebro adolescente, una mente en construcción. Emse Edapp S. L.